Engineering
When you are tasked with operating downhole tools in some of the world’s most difficult drilling enviornments you need to make sure you have the best tools. We understand at Rapid it all starts with the quality of the tool. This is our core focus; to build bettter tools. Rapid ensures that you, as a service provider, are getting the expertise you need in delivering some of the world’s most advanced, high performing, cost effective tools in the world. Rapid does this by an investment in its people, their experience, and the ability to deliver some of the advanced engineering available along with state of the art manufacturing & testing facilities.
Utilizing over 200 years of engineering experience in downhole tools Rapid starts all developments with extensive computer dynamic modeling. This modeling consists of but is not limited to:
-
FEA (Finite Element Analysis)
-
CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics)
-
Non proportional loading calculations
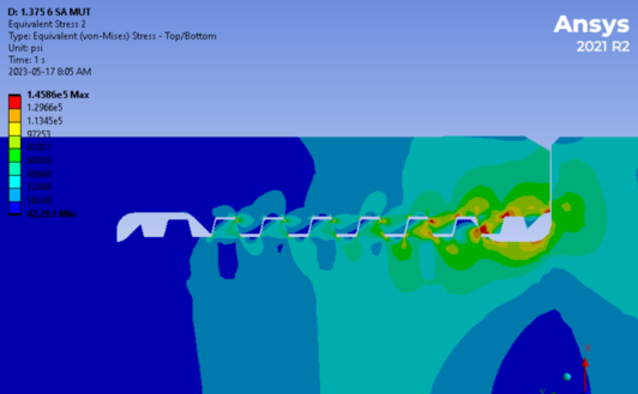
FEA (Finite Element Analysis) is a numerical method used to analyze complex structures and systems in engineering. It uses numerical techniques to perform a mathematical analysis of a physical system and predict its behavior under different conditions and loads. The FEA process involves dividing the complex system into smaller, simpler parts (called finite elements), which can be analyzed separately. Each finite element is subjected to mathematical equations that represent the behavior of the system under different physical conditions and loads. The results obtained from the FEA analysis provide valuable insights into the behavior of the system, including the stresses, strain, deformation, and vibrations that it experiences. This information is crucial for engineers and designers to optimize the system’s performance, durability, and safety. FEA analysis is commonly used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, civil engineering, and manufacturing. It can be used to analyze structures such as bridges, buildings, and aircraft, as well as components like engine parts, gear systems, and electrical circuits. Overall, FEA analysis is a powerful tool for engineers and designers to optimize their designs and ensure the safety and reliability of the systems they create.
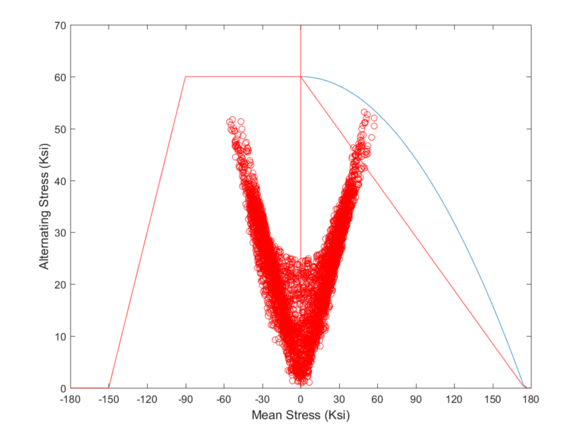
ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) defines Non-Proportional Loading as a type of loading condition in material testing, where the stress and strain don’t have a linear relationship with each other. In other words, the load is not applied gradually, or in equal increments, but fluctuates intermittently due to different factors such as a sudden shock, cyclic stress, or unsteady load application. In Non-Proportional Loading, each cycle of stress can cause a different amount of strain on the material, leading to plastic deformation or fatigue failure. The non-proportional nature of the loading also affects the material’s elastic and plastic behavior, and it is essential to consider it when designing and testing the mechanical properties of material
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modeling is a numerical simulation technique used to study the behavior of fluids and their interaction with solid surfaces. It involves the use of algorithms and mathematical models to solve fluid flow problems and understand the behavior of fluids.
CFD modeling allows engineers and scientists to simulate complex fluid behavior, including turbulence, heat transfer, and chemical reactions. It is used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, energy, and biomedical engineering. CFD modeling can help optimize designs, reduce costs, and improve performance in these industries.
Manufacturing
Located in Leduc Alberta, Rapid has a state of the art manufacturing and testing facility with over 60,000 sq.ft dedicated to the manufacturing of downhole tools. Owning our manufacturing facility is paramount in creating advanced tools cost effectively